Driving licence codes and categories explained
If you hold a UK driving licence, you may have wondered what the various letters and numbers printed on the back of your licence mean.
At first glance, these could be mistaken for random characters. However, in reality, they convey important information about the type(s) of vehicles that you are authorised to drive with your current licence.
In this comprehensive guide, we will list and explain all the codes and categories detailed on UK driving licences. We’ll also clarify which licence categories apply to cars, motorcycles and other vehicle types.
Finally, we’ll cover the various penalty codes that can be applied to your licence, how many points you may incur for each offence – and how long these points will stay on your licence.
It’s important to understand driving codes and categories, as this could help you identify an error on your licence. What’s more, if you’re planning a road trip that involves crossing borders, you could be asked questions by officials checking your licence. So, it’s good to be prepared.
Read on to ensure your knowledge is up to scratch!
Get a free valuation
What are the driving licence codes and categories?
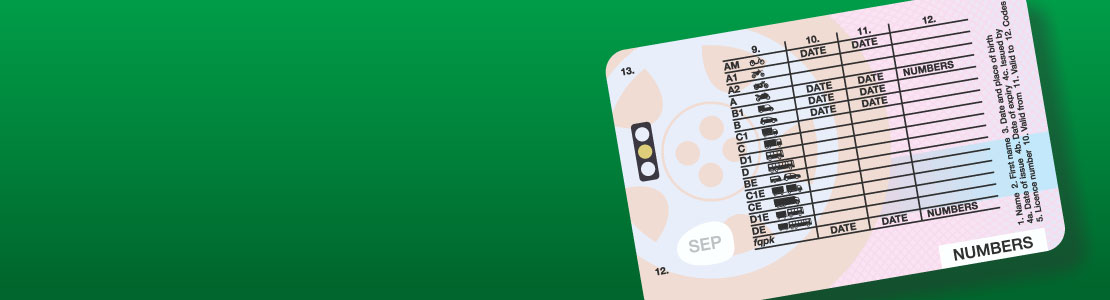
The numbers and letters on the back of your UK driving licence make up two types of information:
Driving licence categories
These indicate the type(s) of vehicles that you can drive and are made up of both letters and numbers.
Driving licence codes
These indicate the requirements that you must meet to drive safely and are made up of numbers only.
Full list of driving licence codes
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 01 | Eyesight correction (glasses, contact lenses, etc.) |
| 02 | Hearing or communication aid |
| 10 | Modified transmission |
| 15 | Modified clutch |
| 20 | Modified braking systems |
| 25 | Modified accelerator systems |
| 30 | Combined braking and accelerator systems (licences issued before 2016 only) |
| 31 | Pedal adaptations and/or safeguards |
| 32 | Combined service brake and accelerator systems |
| 33 | Combined service brake, accelerator and steering systems |
| 35 | Modified control layouts |
| 40 | Modified steering |
| 42 | Modified rear-view mirror(s) |
| 43 | Modified driving seats |
| 44 | Modifications to motorbikes |
| 44 (1) | Single operated brake |
| 44 (2) | Adapted front wheel brake |
| 44 (3) | Adapted rear wheel brake |
| 44 (4) | Adapted accelerator |
| 44 (5) | (Adjusted) manual transmission and manual clutch |
| 44 (6) | (Adjusted) rear-view mirror(s) |
| 44 (7) | (Adjusted) commands (direction indicators, braking light, etc.) |
| 44 (8) | Seat height allowing the motorcycle driver to have two feet on the ground at the same time and balance the vehicle when stopped and standing |
| 44 (11) | Adapted foot rest |
| 44 (12) | Adapted hand grip |
| 45 | Motorbikes only with sidecar |
| 46 | Tricycles only (licences issued before 29th June 2014 only) |
| 70 | Exchange of licence |
| 71 | Duplicate of licence |
| 78 | Restricted to vehicles with automatic transmission |
| 79 | Restricted to vehicles in conformity with the specifications stated in brackets on your licence |
| 79 (2) | Restricted to category AM vehicles of the 3-wheel or light quadricycle type |
| 79 (3) | Restricted to tricycles |
| 96 | Allowed to drive a vehicle and trailer where the trailer weighs at least 750kg and the combined weight of the vehicle and trailer is between 3500kg and 4250kg |
| 97 | Prohibited from driving category C1 vehicles which must have a tachograph fitted |
| 101 | Not for hire or reward |
| 102 | Drawbar trailers only |
| 103 | Subject to certificate of competence |
| 105 | Vehicle is no more than 5.5 metres long |
| 106 | Restricted to vehicles with automated transmissions |
| 107 | No more than 8250kg |
| 108 | Subject to minimum age requirements |
| 110 | Limited to transporting persons with restricted mobility |
| 111 | Limited to 16 passenger seats |
| 113 | Limited to 16 passenger seats except for automatics |
| 114 | With any special controls required for safe driving |
| 115 | Organ donor |
| 118 | Start date is for earliest entitlement |
| 119 | Weight limit does not apply |
| 121 | Restricted to conditions specified in the Secretary of State’s notice |
| 122 | Valid on successful completion of basic moped training course |
| 125 | Tricycles only (for licences issued before 29th June 2014 only) |
Why are there different types of driving licences?
Different vehicles require different driving licences due to each vehicle type having its own rules, regulations and requirements that drivers must meet, with most vehicle types even requiring them to pass dedicated tests.
For example, you need to obtain a different licence to drive a HGV (heavy goods vehicle) than to drive a car, due to the difference in handling for these much larger vehicles.
What categories are covered on my driving licence?
Once you receive your full UK driving licence, you have clearance to drive the following vehicles:
- Cars (manual and automatic).
- Motorbikes.
- 2 and 3-wheeled vehicles.
- 4-wheeled vehicles.
- Light quad bikes.
- Trailers.
- Tractors.
- Ride-on lawnmowers.
- Pedestrian controlled vehicles.
It’s important to check the specific eligibility requirements for each one of these vehicles before attempting to drive them. For example, under a standard UK driving licence, the clearance to drive 4-wheeled vehicles only applies to light goods vehicles up to 550kg.

Which driving licence categories apply to cars?
Below are the driving licence categories which apply to cars and light vehicles, such as trailers.
B
A Category B licence covers you to drive a motor vehicle up to 3500kg in weight with as many as 8 passenger seats. A trailer weighing up to 750kg may also be added to the vehicle.
Before towing a caravan or trailer for the first time, you can use our towing capacity calculator to check that your vehicle can safely tow the intended load.
B Auto
The Category B Auto licence has the same conditions as a Category A, except you are only able to drive vehicles with automatic transmission. If you wish to drive both manual and automatic vehicles, you must learn to drive and take your practical test using a manual vehicle.
BE
A Category BE (or B+E) licence allows you to drive a Category B vehicle and a trailer or semi-trailer which does not meet Category B regulations. The maximum mass of the trailer alone under this category must be no more than 3500kg.
B1
Under a Category B1 licence, you can drive 4-wheeled vehicles with up to 400kg unladen weight (or 550kg for vehicles designed for carrying goods).
Which driving licence categories apply to motorbikes?
The following driving licence categories apply more specifically to motorcycles and mopeds.
A
A Category A licence allows you to use bikes with power exceeding 35kW and tricycles exceeding 15kW. You must be 21 or over to receive this licence.
A1
The Category A1 licence clears you to ride a light motorcycle with an engine size of up to 125cc, a power output of up to 11kW - and a power-to-weight ratio of no more than 0.1kW/kg. This category also covers tricycles with a power ratio of 15kW.
A2
The Category A2 licence allows you to ride a motorcycle with a power output of up to 35kW – and with a power/weight ratio of up to 0.2kW/kg. You must be at least 19 years of age to acquire this licence.
AM
The Category AM licence allows you to use four-wheeled vehicles of up to 350kg (unladen weight). This category previously covered mopeds, two-wheeled and three-wheeled vehicles.
P
The Category P licence allows you to drive two-wheeled vehicles with design speeds between 28mph and 31mph, with an engine size of up to 50cc.
Q
The Category Q licence covers the driving of two-wheeled and three-wheeled vehicles with no pedals. The engine size must be no more than 50cc and the vehicle must have a maximum design speed no more than 15.5mph.
Other driving licence categories
We have listed the driving licence categories that cover vehicles other than cars and motorbikes below. You must be at least 21 to acquire many of these licences.
D
A Category D licence allows the holder to drive a bus or coach with more than 8 passenger seats, with a maximum trailer weight of up to 750kg.
D1
A Category D1 licence allows you to drive a minibus with up to 16 passenger seats and a maximum length of 8 metres. With this licence, you can also tow a trailer up to 750kg in weight.
D1E
The Category D1E (D1+E) licence allows you to drive a D1 category minibus with a trailer weighing up to 750kg. The combined weight of both must not exceed 12,000kg.
F
The Category F licence allows you to drive agricultural tractors with no restrictions. In many cases, you will already be eligible to do this with a Category B licence.
G
You’ll need to acquire a Category G licence to drive a steamroller or diesel-driven road roller.
H
The Category H licence covers civilian tracked vehicles, such as former military vehicles.
K
The Category K licence allows you to drive a ride-on lawnmower (or other pedestrian-controlled vehicles). As with Category F, there’s a good chance that you are already eligible to do this using a Category B licence.
L
The Category L licence allows you to drive electrically propelled vehicles.
M
Category M licences allow you to drive trolley vehicles.
N
A Category N licence indicates that you are permitted to drive a vehicle that is ‘exempt from duty’. These vehicles are permitted to cover short distances on the road but are unlikely to do so. Forklifts are a common example of a Category N vehicle.
Driving licence penalty codes
Penalty points (along with speeding fines and fines to avoid when selling your old car) are among the penalties that can apply if you are caught breaking a motoring law.
If you are convicted of a motoring offence, the courts can endorse your driving licence with penalty points, which will stay on your record for either 4 or 11 years. How long points stay on your licence will depend on the type of offence committed.
You can check the number of points on your driving licence via the Gov.uk website.
If you commit a driving offence, you may receive between 1 and 11 penalty points – and the more serious the offence, the more points you’ll receive.
Every driving licence penalty has its own unique penalty code. You’ll find a comprehensive list in the table below.
Each code is a combination of letters and numbers, with the two letters at the start corresponding to the type of offence (for example, ‘AC’ for accident offences or ‘DD’ for dangerous driving).
| Code | Offence | Penalty points | Time on licence |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC10 | Failing to stop after an accident | 5 to 10 | 4 years from offence |
| AC20 | Failing to give particulars or report an accident within 24 hours | 5 to 10 | 4 years from offence |
| AC30 | Undefined accident offences | 4 to 9 | 4 years from offence |
| BA10 | Driving while disqualified by order of court | 6 | 4 years from offence |
| BA30 | Attempting to drive while disqualified by order of court | 6 | 4 years from offence |
| BA40 | Causing death by driving while disqualified | 3 to 11 | 4 years from conviction |
| BA60 | Causing serious injury by driving while disqualified | 3 to 11 | 4 years from conviction |
| CD10 | Driving without due care and attention | 3 to 9 | 4 years from offence |
| CD20 | Driving without reasonable consideration for other road users | 3 to 9 | 4 years from offence |
| CD30 | Driving without due care and attention or without reasonable consideration for other road users | 3 to 9 | 4 years from offence |
| CD33 | Causing serious injury by careless or inconsiderate driving | 3 to 9 | 4 years from offence |
| CD40 | Causing death through careless driving when unfit through drink | 3 to 11 | 11 years from conviction |
| CD50 | Causing death by careless driving when unfit through drugs | 3 to 11 | 11 years from conviction |
| CD60 | Causing death by careless driving with alcohol level above the limit | 3 to 11 | 11 years from conviction |
| CD70 | Causing death by careless driving then failing to supply a specimen for alcohol analysis | 3 to 11 | 11 years from conviction |
| CD80 | Causing death by careless or inconsiderate driving | 3 to 11 | 4 years from conviction |
| CD90 | Causing death by driving while unlicensed, disqualified or uninsured | 3 to 11 | 4 years from conviction |
| CU10 | Using a vehicle with defective brakes | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| CU20 | Causing or likely to cause danger by reason of unsuitable vehicle or using a vehicle with parts/accessories in a dangerous condition | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| CU30 | Using a vehicle with defective tyres | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| CU40 | Using a vehicle with defective steering | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| CU50 | Causing or likely to cause danger by reason of load or passengers | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| CU80 | Breach of requirements as to control of the vehicle, such as using a mobile phone while driving | 3 to 6 | 4 years from offence |
| DD10 | Causing serious injury through dangerous driving | 3 to 11 | 4 years from conviction |
| DD40 | Dangerous driving | 3 to 11 | 4 years from conviction |
| DD60 | Manslaughter or culpable homicide while driving a vehicle | 3 to 11 | 4 years from conviction |
| DD80 | Causing death by dangerous driving | 3 to 11 | 4 years from conviction |
| DD90 | Furious driving | 3 to 9 | 4 years from conviction |
| DR10 | Driving or attempting to drive with alcohol above limit level | 3 to 1.1 | 11 years from conviction |
| DR20 | Drink driving or attempting to drive while unfit through drink | 3 to 11 | 11 years from conviction |
| DR30 | Driving or attempting to drive then failing to supply a specimen for analysis | 3 to 11 | 11 years from conviction |
| DR31 | Driving or attempting to drive then refusing to give permission for analysis of a blood sample that was taken without consent due to incapacity | 3 to 11 | 11 years from conviction |
| DR61 | Refusing to give permission for analysis of a blood sample that was taken without consent due to incapacity in circumstances other than driving or attempting to drive | 10 | 11 years from conviction |
| DR40 | In charge of a vehicle while alcohol level above limit | 10 | 4 years from offence |
| DR50 | In charge of a vehicle while unfit through drink | 10 | 4 years from offence |
| DR60 | Failure to provide a specimen for analysis in circumstances other than driving or attempting to drive | 10 | 4 years from offence |
| DR70 | Failing to co-operate with a preliminary test | 4 | 4 years from offence |
| DG10 | Driving or attempting to drive with drug level above the specified limit | 3 to 11 | 11 years from conviction |
| DG60 | Causing death by careless driving with drug level above the limit | 3 to 11 | 11 years from conviction |
| DR80 | Driving or attempting to drive when unfit through drugs | 3 to 11 | 11 years from conviction |
| DG40 | In charge of a vehicle while drug level above specified limit | 10 | 4 years from offence |
| DR70 | Failing to co-operate with a preliminary test | 4 | 4 years from offence |
| DR90 | In charge of a vehicle when unfit through drugs | 10 | 4 years from offence |
| IN10 | Using a vehicle uninsured against third party risks | 6 to 8 | 4 years from offence |
| LC20 | Driving otherwise than in accordance with a licence | 3 to 6 | 4 years from offence |
| LC30 | Driving after making a false declaration about fitness when applying for a licence | 3 to 6 | 4 years from offence |
| LC40 | Driving a vehicle having failed to notify a disability | 3 to 6 | 4 years from offence |
| LC50 | Driving after a licence has been cancelled, revoked or refused on medical grounds | 3 to 6 | 4 years from offence |
| MS10 | Leaving a vehicle in a dangerous position | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| MS20 | Unlawful pillion riding | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| MS30 | Play street offences | 2 | 4 years from offence |
| MS50 | Motor racing on the highway | 3 to 11 | 4 years from offence |
| MS60 | Offences not covered by other codes | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| MS70 | Driving with uncorrected defective eyesight | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| MS80 | Refusing to submit to an eyesight test | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| MS90 | Failure to give information regarding the identity of the driver | 6 | 4 years from offence |
| MW10 | Contravention of special roads regulations excluding speed limits | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| PC10 | Undefined contravention of pedestrian crossing regulations | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| PC20 | Contravention of pedestrian crossing regulations with moving vehicle | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| PC30 | Contravention of pedestrian crossing regulations with stationary vehicle | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| SP10 | Exceeding goods vehicle speed limits | 3 to 6 | 4 years from offence |
| SP20 | Exceeding speed limit for type of vehicle excluding goods or passenger vehicles | 3 to 6 | 4 years from offence |
| SP30 | Exceeding statutory speed limit on a public road | 3 to 6 | 4 years from offence |
| SP40 | Exceeding passenger vehicle speed limit | 3 to 6 | 4 years from offence |
| SP50 | Exceeding speed limit on a motorway | 3 to 6 | 4 years from offence |
| TS10 | Failing to comply with traffic light signals | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| TS20 | Failing to comply with double white lines | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| TS30 | Failing to comply with ‘STOP’ sign | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| TS40 | Failing to comply with direction of a constable or warden | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| TS50 | Failing to comply with traffic signs excluding ‘STOP’ signs, traffic lights or double white lines | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| TS60 | Failing to comply with a school crossing patrol sign | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| TS70 | Undefined failure to comply with a traffic direction sign | 3 | 4 years from offence |
| UT50 | Aggravated taking of a vehicle | 3 to 11 | 4 years from offence |
| TT99 | Total penalty points on licence reaching 12 or more in 3 years period | Disqualification from driving, code TT99 on record | 4 years from conviction |
Frequently Asked Questions
Anyone with a valid Category B licence may drive a van weighing up to 3500kg. However, should you wish to drive a heavy goods vehicle (HGV), you’ll need to apply for a separate HGV licence.
If you hold a standard UK driving licence, you can ride a moped with an engine size of up to 50cc after passing a compulsory basic training (CBT) course. To ride a motorbike with a more powerful engine, you’ll need obtain an A/A1 licence.
Driving on an expired licence is illegal. If you are caught driving with an expired licence, whether you received your DVLA reminder or not, you could face fines or further legal repercussions. It’s your sole responsibility to renew or update your driving licence before its expiry date.
The codes on a provisional driving licence are the same as those on a standard licence.
However, provisional licences only allow you to drive the relevant vehicles whilst being supervised by a driver who is at least 21 years of age and has held a full UK driving licence for three years or more.
Most vehicle hire companies will ask you to produce your driving licence before allowing you to drive away in a hired vehicle.
This is to prevent customers from hiring vehicles that they are not licenced to drive. If you attend a vehicle hire collection without your driving licence, the company may refuse to hand over the keys.
A standard UK driving licence is valid in most European countries. However, you’ll need to acquire an IDP (International Driving Permit) in countries where a UK licence alone is not sufficient.